Types of Touch Screen Monitors: A Complete Beginner’s Guide
Published: 23 Oct 2025
Today, touch screen monitors can be found all around, from smartphones and tablets to ATMs and interactive display devices. They’ve changed how we use technology, making it faster and easier to manage things with a single touch. But did you know there are many different types of touch screen monitors, each designed only for a specific use? Knowing such types helps you to select the best one for your purposes, if it’s for gaming, job, education, or business. This guide will explain how each type works and which one is most ideal for your needs.
Types of Touch Screen Monitors
Touch screen monitors have modified our interaction with electronics, making it easier and more natural. They are available in many different types of forms, like mobile phones, ATMs, and professional displays, to meet a variety of needs. Knowing the different types allow you to choose the best one for your business, gaming, or creative setting.Here are the main types of touch screen monitors:
- Resistive Touch Screen
- Capacitive Touch Screen
- Surface Acoustic Wave (SAW) Touch Screen
- Infrared (IR) Touch Screen
- Optical Imaging Touch Screen
- Acoustic Pulse Recognition (APR) Touch Screen
- Near-Field Imaging (NFI) Touch Screen
- Projected Capacitive (P-Cap) Touch Screen
- Multi-Touch Optical Touch Screen
- In-Cell and On-Cell Touch Screen
Resistive Touch Screen
A resistive touch monitor responds when you lightly press it with your finger, pen, or cursor. It has multiple thin layers which touch with other when pressure is applied, giving a signal to the device. These monitors are reliable and perform well in all kinds of conditions, especially with fingers on.
Uses:
- ATMs and cash machines
- Restaurant order screens
- Industrial control panels
- Medical equipment displays
- Older smartphones and PDAs

Capacitive Touch Screen
A capacitive touch screen works with natural electrical signals from your fingers. You don’t need to click on it hard; a light tap or swipe will be enough. These screens are smooth, fast and very responsive, which is why they are so popular in modern mobile devices. They also provide clear images and accurate performance.
Uses:
- Smartphones and tablets
- Touchscreen laptops
- Interactive kiosks
- Smart home control panels
- Car infotainment systems
Surface Acoustic Wave (SAW) Touch Screen
A Surface Acoustic Wave (SAW) touch screen uses sound waves that travel on the screen surface. When you contact the screen, these waves stop working and the device detects where the touch occurred. These displays are known for their high visibility and quick touch response. They’re perfect for settings that need accuracy and bright displays.
Uses:
- Information kiosks
- Public ticketing machines
- Interactive museum displays
- Retail touch systems
- Office meeting room panels

Infrared (IR) Touch Screen
An Infrared (IR) touch screen uses invisible light beams to build lines across the screen. When you touch it, your finger breaks the light beams, and the system finds the exact spot. It is powerful and long-lasting but it doesn’t depend on pressure or special coatings. These screens work well even with gloves or stylus use.
Uses:
- Interactive whiteboards
- Large digital displays
- Self-service kiosks
- Gaming and entertainment systems
- Public information screens
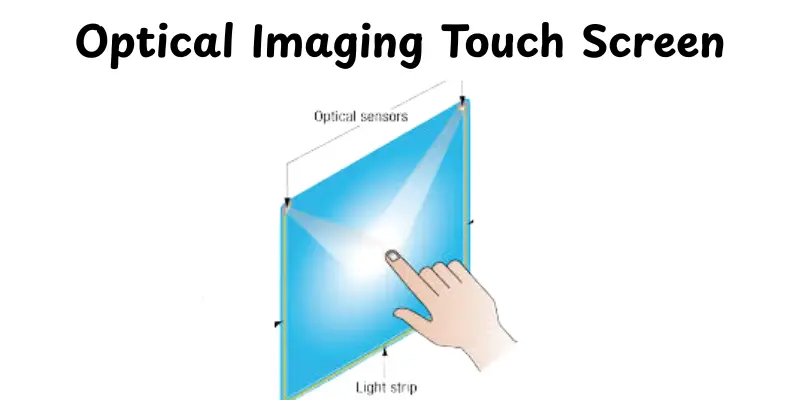
Optical Imaging Touch Screen
An optical imaging touch screen detects your touch with small cameras and infrared light. When you tap the screen, the cameras detect the shadow or reflection to determine the contact point. It works well on larger displays and doesn’t require specific pressure or stylus pens. This makes it easy to use, reliable, and suitable for multiple types of purposes.
Uses:
- Interactive digital boards
- Large display monitors
- Retail and shopping kiosks
- Educational touch panels
- Museum and exhibition displays
Acoustic Pulse Recognition (APR) Touch Screen
An Acoustic Pulse Recognition (APR) touch screen converts sound waves from a touch into signals that the device can detect. When you tap the glass, it produces small sound waves that sensors detect and identify. These screens are reliable, exact, and don’t break out easily because they rely on sound instead of pressure. They are suitable for heavy everyday use.
Uses:
- Banking kiosks and ATMs
- Interactive public displays
- Retail point-of-sale systems
- Industrial control panels
- Office meeting room screens
Near-Field Imaging (NFI) Touch Screen
A Near-Field Imaging (NFI) touch screen detects changes in electric fields when you touch the surface. It needs no pressure or light to function, making it highly reliable and long-lasting. These displays can detect touches through gloves and other materials. They’re useful for tough environments where regular touch panels can fail.
Uses:
- Industrial control systems
- Medical monitoring devices
- Outdoor ATMs and kiosks
- Military and defense equipment
- Public information terminals
Projected Capacitive (P-Cap) Touch Screen
One of the most common types of touch screens seen in current devices is projected capacitive (P-Cap). It works by detecting electrical signals from your fingertips, even through thin glass. These displays are fast, smooth, and highly accurate, making them ideal for multi-touch actions like zooming and swiping. They’re also tough and scratch-resistant.
Uses:
- Smartphones and tablets
- Touchscreen laptops
- Interactive kiosks
- Automotive touch panels
- Smart home control devices
Multi-Touch Optical Touch Screen
A Multi-Touch Optical Touch Screen detects many touch places at once using cameras or sensors placed carefully around the screen. It can easily track actions like clicking, zooming, and rotating, making it very interactive. These panels are ideal for huge displays where several people can use them continuously. They’re exact, durable and simple to maintain.
Uses:
- Interactive classroom boards
- Retail and shopping kiosks
- Museum and exhibition displays
- Large conference room screens
- Public information terminals
In-Cell and On-Cell Touch Screen
An In-Cell and On-Cell Touch Screen combines touch sensors directly within or on top of the display panel. The design makes the screen smaller, lighter, and more responsive than normal touch monitors. It also increases image clarity and reduces reflections. These displays are commonly seen in slim, high-end devices with the focus on smooth performance and clean design.
Uses:
- Modern smartphones
- High-end tablets
- Ultrabook laptops
- Smartwatches
- Advanced car displays
The Best Type of Touch Screen Monitor
If you’re looking for the best type of touch screen monitor, get one with Projected Capacitive (P-Cap) technology. It feels smooth, responds fast, and supports multi-touch action with ease. The screen keeps clear, durable and attractive – perfect for both work and play. Personally, I suggest it to anyone looking for a modern, dependable, and simple touch experience every time.
Conclusion
Understanding the many types of touch screen monitors helps you to select the best one for your needs. Each type, such as resistive, capacitive, infrared, and optical, functions specifically and is most suited for specific uses. Some are suitable for accurate work and durability, but others give speed and smooth motions. Knowing this type of information helps you choose a monitor that specifically fits your work style, environment, and comfort level.
FAQs
A touch screen is a display that understands your touch. It can make use of resistive, capacitive, infrared, and surface acoustic wave technologies. You can tap, click, and drag things on the screen without needing a mouse or keyboard.
The five main types are resistive, capacitive, infrared (IR), surface acoustic wave (SAW), and optical touch panels. Each works differently to detect touch. Some are more accurate, while others are longer-lasting or easier to use.
Choose based on your needs. A capacitive screen is ideal for use in the office or everyday. If you need something durable for industrial applications, resistive is better. For interactive displays, infrared or optical types work well.
Yes, capacitive and projected capacitive (P-Cap) screens are best for multi-touch gestures. They can easily detect several fingers at once. This makes them perfect for smartphones, tablets, and modern touch monitors.
Resistive touchscreens work well with gloves or a stylus. Capacitive displays typically need bare fingertips, but some advanced models now support special gloves or styluses. Always double-check your device’s parameters for perfect accuracy.
Not all types do well under sunshine. Capacitive and infrared touch displays usually work better outdoors. Resistive screens can be difficult to see in bright light unless they have an anti-glare layer.

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks