What is Microcomputer? Discover Its Impact on Modern Technology
Published: 11 Dec 2025
Microcomputers are a key part of modern life, powering everything from smartphones to personal computers.In this guide, we’ll explore what is microcomputer and how they fit into our daily activities.We’ll look at their key features, different types and how they are used in various fields.By the end, you’ll have a better understanding of why microcomputers are essential in today’s technology-driven world.To further explore the different options available, check out our guide on the types of computer, where we discuss various computer categories and their unique features.
What Is Microcomputer?
A microcomputer is a small, general-purpose computer designed for individual use.It usually has a central processing unit (CPU), memory, storage, and input/output devices like a keyboard and screen.Microcomputers are powered by microprocessors, which are tiny chips that perform most of the tasks.These computers are affordable and compact, making them perfect for personal work, gaming and learning.Examples of microcomputers include desktop PCs, laptops, and even smartphones.They are widely used in homes, schools, and businesses around the world.

How Does a Microcomputer Work?
A microcomputer works by following a simple process of input, processing and output.It takes data from the user, processes it with the help of its components and then displays or stores the result.Let’s break down how this work step by step:
- Input: The user provides data through input devices like a keyboard, mouse or microphone.
- Processing: The Central Processing Unit (CPU) takes the input data and performs calculations or operations on it. The CPU is like the brain of the microcomputer.
- Memory: The microcomputer uses RAM (temporary memory) to store data while it’s working.It also uses storage devices like hard drives or SSDs to save data permanently.
- Output: Once the data is processed, the results are shown on output devices like a monitor, printer, or speakers.
- Control: The operating system (OS) manages everything, making sure that the hardware and software work together smoothly.
Parts of a Microcomputer
A microcomputer is made up of several key parts that work together to make it function.Each part has its own work and contributes to the overall performance of the system.Here’s a breakdown of the main parts of microcomputer:
- Central Processing Unit: The brain of the microcomputer.It processes instructions and controls all the activities of the computer.
- Motherboard: The main electrical board links all of the computer’s components. It helps communication between the CPU, memory, and other components.
- Memory (RAM): Temporary storage that holds data and instructions the CPU is currently using.The more RAM, the better the computer can multitask.
- Storage (Hard Drive/SSD): Stores all your files, programs and the operating system. SSDs are faster than traditional hard drives.
- Power Supply: Provides electrical power to all the components of the microcomputer.
- Input Devices: Tools that allow you to give commands to the computer.Examples include the keyboard, mouse and microphone.
- Output Devices: These show you the result of the computer’s work.Common output devices are the monitor, printer and speakers.
- Graphics Card (GPU): Handles the display of images and videos.Important for gaming or video editing.
- Cooling System: Keeps the computer from overheating, usually using fans or heat sinks.
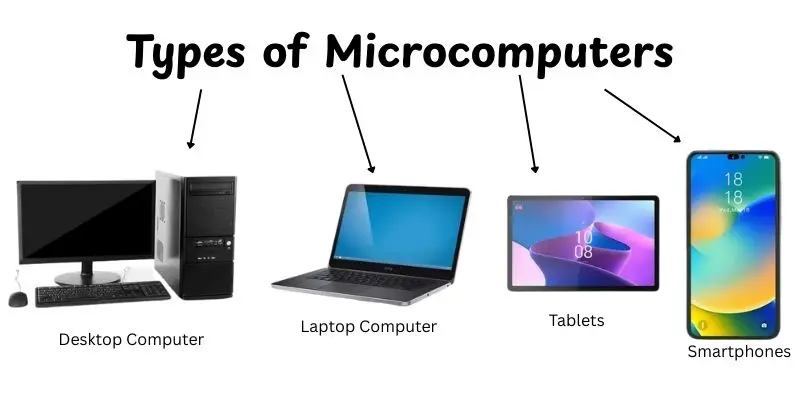
Types of Microcomputers
Microcomputers come in different shapes and sizes, each designed for specific tasks. Whether you’re using one at home, school, or work, there are several types of microcomputers to choose from.Let’s take a look at the main types:
- Desktop Computers: These are the traditional, stationary computers that sit on a desk.They have all the essential components and are good for work, gaming, and general use.
- Laptop Computers: Laptops are portable, compact and have all the features of a desktop. They’re great for people who need to work or study on the go.
- Tablets: These are lightweight and portable devices with a touchscreen.Tablets are great for reading, browsing the web, or watching videos.
- Smartphones: Small, pocket-sized devices that are basically microcomputers.They let you do many of the same things as a computer, like browsing, gaming and using apps.
- Embedded Systems: These are small microcomputers built into other devices like cars, refrigerators and smartwatches.They perform specific tasks but don’t have a full operating system like a PC.
- Single Board Computers (SBCs): Small computers like Raspberry Pi that are often used for learning, DIY projects or in small appliances and robots.
Features of Microcomputer
Microcomputers come with a range of features that make them suitable for personal use, work, and entertainment. Here are some key features:
- Compact Size: Microcomputers are small and portable, making them easy to carry or fit into tight spaces.
- Affordability: They are budget-friendly compared to larger systems like mainframes or minicomputers.
- User-Friendly: Microcomputers are designed to be easy to use, with simple interfaces that anyone can navigate.
- High Performance for Everyday Tasks: They can handle tasks like browsing, word processing, and gaming without slowing down.
- Processing Power: Equipped with processors (CPUs) that handle calculations and instructions, enabling smooth performance.
- Memory and Storage: Microcomputers include RAM for temporary data storage and hard drives or SSDs for permanent storage.
- Connectivity: Most microcomputers support internet and wireless connectivity, allowing you to access online resources and connect with other devices.
- Versatility: They can be used for a variety of applications like office work, entertainment, gaming, and creative tasks.
- Compatibility: Microcomputers support a wide range of software, from operating systems like Windows or macOS to various apps and programs.
Uses / Where We See Microcomputers
Microcomputers are everywhere! They’ve become an important part of our daily lives, helping us with work, entertainment and even in things we might not notice. Here are some common places and ways we see microcomputers in action:
- In Homes: Used for tasks like browsing the internet, managing finances, watching movies and staying in touch with friends and family.
- In Education: Microcomputers are essential in schools and universities, where they are used for research, learning and online courses.
- In Offices: From word processing to email and spreadsheets, microcomputers help with administrative work, presentations and communication.
- In Smartphones and Tablets: These portable devices are small, powerful microcomputers used for calling, texting, gaming, browsing and many more tasks.
- In Entertainment: Used for gaming consoles, music players and streaming services, microcomputers make entertainment more interactive and fun.
- In Cars: Microcomputers control systems like navigation, entertainment and even safety features such as airbags.
- In Home Appliances: Items like smart refrigerators, washing machines and thermostats are powered by microcomputers to make them more efficient and connected.
- In Medical Devices: Used in equipment like heart monitors and diagnostic tools to collect and analyze patient data.
- In Embedded Systems: Microcomputers are found in everyday gadgets like smartwatches, security cameras and kitchen appliances, performing specific tasks efficiently.

Advantages and Disadvantages of Microcomputers
In this section, we will look at the pros and cons of microcomputers. Understanding both will help you decide when and where to use them.
| Advantages of Microcomputers |
|---|
|
| Disadvantages of Microcomputers |
|---|
|
Tips for Choosing a Microcomputer
Choosing the right microcomputer depends on your needs, preferences and budget.Here are some tips to help you make the best decision:
- Determine Your Purpose: Think about what you’ll use the microcomputer for. Is it for general tasks like browsing and word processing, or do you need something for gaming or video editing?
- Consider the Performance: Look for a computer with a good processor (CPU) and enough RAM. More powerful processors and more RAM will make your computer perform quicker and handle more tasks effectively.
- Storage Space: Choose a microcomputer with enough storage for your files and programs.SSDs are speedier than regular hard drives (HDDs), but they can be more expensive.
- Portability: If you need to carry your computer around, a lightweight laptop or tablet might be the best choice. If you plan to use it at home, a desktop could work fine.
- Battery Life: For laptops or tablets, check the battery life. A longer battery life will keep you productive on the go without needing to charge often.
- Screen Size and Display: Decide on the size of the screen based on how you’ll use it. Larger screens are better for tasks like editing photos or watching videos, while smaller screens are more portable.
- Operating System: Choose an operating system that you’re comfortable with, whether it’s Windows, macOS, or a different system like Linux.Each has its own set of features and compatibility.
- Budget: Set a budget and stick to it. Microcomputers come in a wide range of prices, so find one that offers good value for the features you need.
Conclusion
We’ve covered a lot about what is microcomputer in this guide, from their basic functions and different types to how they’re used in everyday life.We also discussed their advantages and disadvantages, along with tips to help you choose the right one.
If you’re in the market for a new device,I recommend thinking about what you really need, like portability, power, or price, before you make a choice.Microcomputers are super versatile and can serve a lot of purposes, so choosing the right one will make a big difference in your experience.Alright, folks, keep learning and stay tuned for more helpful tips coming your way!
FAQs
Here are five common examples of microcomputers:
- Desktop PCs: Traditional computers used in homes and offices.
- Laptops: Portable computers that are easy to carry around.
- Smartphones: Small, handheld devices that function like microcomputers.
- Tablets: Portable devices with touchscreens, used for browsing and apps.
- Raspberry Pi: A small, affordable computer used for learning and DIY projects.
A microcomputer is a small, personal computer designed for individual use. It typically includes a central processing unit (CPU), memory, storage, and input/output devices like a keyboard and monitor. Microcomputers are affordable, compact, and widely used in homes, schools, and businesses.
A microcomputer has a processor (CPU) that does the computing tasks.It also has memory and storage for data, plus input and output devices like a keyboard and screen.All parts work together to run programs and tasks.

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks