Examples of Digital Computers: A Guide for Beginners
Published: 27 Jan 2026
A digital computer is an electronic device that takes information, processes it using binary code (0s and 1s), and gives results quickly and accurately. Modern devices like smartphones, desktops, laptops, and servers are examples of digital computers. These computers are everywhere, helping us with communication, work, and entertainment. Digital clocks, ATMs, and calculators are other common examples that show how digital computing technology appears in everyday tools. These devices store, retrieve, and manipulate data to solve problems and run applications. Understanding basic examples of digital computers helps us see how central they have become in schools, businesses, and homes around the world

Everyday Examples of Digital Computers
Digital computers are everywhere, making our lives easier and more efficient. They power smartphones, laptops, and even everyday devices like weighing scales. These computers help us complete tasks quickly and smoothly, whether at home, work, or on the go.Here’re some examples of digital computers:
- Smartphones
- Personal Computers and Laptops
- Digital Watches and Clocks
- Calculators
- Automated Teller Machines (ATMs)
- Vehicles (Cars)
- Banking and Finances
- Self-Scan Machines
- Consumer Electronic Equipments
- Digital Televisions
- Digital Pianos
- Weighing Scales
Smartphones
Smartphones are powerful, compact devices that serve as both communication tools and versatile computers. They run on full operating systems like Android or iOS, allowing users to install various apps for everything from social media to work productivity. These devices are built with the same components as a digital computer, such as a CPU, memory, storage, and input/output systems, making them highly capable of processing complex tasks quickly.
Key Features:
- Touchscreen Interface: The touchscreen allows direct interaction with apps and software, making it user-friendly and efficient.
- Multimedia and Connectivity: Smartphones offer internet access, cameras, GPS, and media playback, essentially functioning as portable computing hubs.
- App Ecosystem: With access to thousands of apps, smartphones provide a wide range of functions, making them adaptable to different needs and tasks.
Personal Computers and Laptops
A laptop or personal computer is examples of digital computers designed for individual use. Laptops are portable and can be used anywhere, while desktops are meant to sit on desks, offering a more stationary setup. These computers help people with work, studying, entertainment, and everyday tasks. The main benefit of personal computers is that they give users access to computing power for simple tasks like typing documents, browsing the internet, running software, and storing data.
Key Features:
- Portability (for laptops): Laptops are lightweight and run on batteries, so you can take them and use them anywhere, whether at home, in the office, or at school.
- Single-User Design: Personal computers are made for one person to use at a time, making them great for individual tasks like writing, learning, and browsing the web.
- Versatility: PCs can run a wide range of software, from productivity tools like spreadsheets to entertainment apps like games and video players, making them useful for both work and fun.
Digital Watches and Clocks
Digital watches and clocks are timekeeping devices that display time using numbers instead of traditional hands. They rely on electronic components like quartz crystals or oscillators, which keep time very accurately. This makes them more precise than older mechanical timepieces. Digital devices are easy to read, with a clear display of hours, minutes, and seconds. Many models also offer extra features, such as alarms, timers, calendars, and even sensors in smart versions. Whether it’s a bedside alarm clock or a wristwatch, digital timepieces are popular in everyday life due to their convenience and flexibility.
Key Features:
- Clear numeric display: Digital watches and clocks show the time in numbers, making it easier for many people to read than an analog clock.
- Electronic timekeeping: They use stable electronic oscillators, like quartz crystals, to measure time accurately and reliably.
- Extra functions: Many digital models offer features like alarms, timers, calendars, or even advanced sensors in smart watches.

Calculators
A digital calculator is examples of digital computers used to perform mathematical operations quickly and accurately. It can handle basic tasks like addition and subtraction, as well as more complex functions such as square roots and percentages. Calculators are common in daily life and are often used by students, professionals, and anyone who needs to do quick math. They are usually small, lightweight, and powered by batteries or solar cells.
Key Features:
- Fast and Accurate: Calculators solve math problems instantly and correctly, making them helpful for school, work, and everyday tasks.
- Portable and Easy to Use: Most calculators are small enough to fit in your pocket or backpack, and their simple buttons make them easy to operate.
- Wide Range of Functions: From basic math to scientific functions like exponents and trigonometry, many calculators offer different features depending on the model.
Automated Teller Machines (ATMs)
An Automated Teller Machine (ATM) is a self-service device that allows people to handle basic banking tasks without visiting a bank or talking to a teller. These machines are connected to secure banking systems, making it easy for customers to withdraw cash, check account balances, deposit money, and transfer funds, all with just a card and PIN. ATMs can be found in banks, malls, airports, and many other public places, offering convenient access to banking services, often 24/7.
Key Features:
- Self-Service Banking: Users can easily withdraw cash, make deposits, or check their account balances on their own, without needing assistance from a bank employee.
- Card and PIN Security: ATMs require a debit or credit card and a PIN for security, ensuring only the cardholder can access their account.
- 24/7 Availability: Most ATMs are available around the clock, giving users access to their money anytime they need it.

Vehicles (Cars)
Modern cars are much more than just machines. They’re packed with digital computers that help control and monitor important systems. Today’s vehicles use many electronic control units (ECUs) and processors to manage everything, from how the engine runs to safety features and entertainment systems. These computers gather data from sensors around the car and make real-time adjustments to keep the car running smoothly, efficiently, and comfortably. This change has made driving safer, cleaner, and much more high-tech than ever before.
Key Features:
- Multiple Computer Systems: Cars today have several computer units controlling things like braking, fuel injection, and stability systems.
- Engine & Safety Control: ECUs help manage engine performance and safety features such as anti-lock brakes (ABS) and airbags.
- Integrated Sensors: Car computers use sensors throughout the vehicle to collect data and make adjustments for improved performance and efficiency.
Banking and Finances
Digital computers are examples of digital computers that crucial in modern banking and finance. They help both customers and banks manage money quickly, accurately, and securely. With computers, customers can check their account balances, transfer funds, pay bills, and view transaction histories online. Banks also use computers to store customer data, process transactions, and reduce mistakes in financial records. In short, computers have changed the way banking works, making it faster and more accessible than ever.
Key Features:
- Account Management & Transactions: Computers let customers view their balances, transfer money, and pay bills instantly on secure online platforms.
- Data Storage & Security: Banks securely store large amounts of customer information, improving both accuracy and safety.
- Efficiency & Speed: Automation of tasks like transfers and record-keeping cuts down on human error and speeds up banking operations.
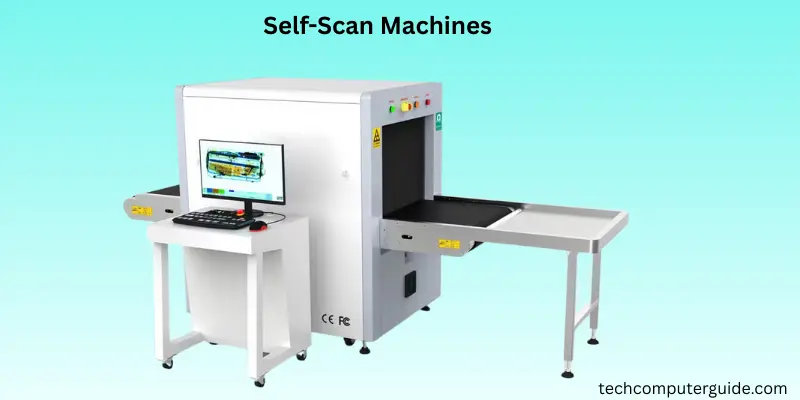
Self-Scan Machines
Self-checkout machines are becoming more common in retail stores and supermarkets. These machines let customers scan and pay for their own items without needing help from a cashier. They include barcode scanners, touchscreens, and payment systems that make the checkout process faster and easier. This technology is part of a bigger trend where customers can do things themselves, helping to reduce long lines and making shopping more convenient. More and more stores are using self-checkout to speed up transactions and offer a more modern shopping experience.
Key Features:
- Faster Checkout & Convenience: Customers can scan their items, pay, and complete the purchase on their own, which helps reduce wait times and makes shopping quicker.
- Multiple Payment Options: Self-checkout machines accept cash, card, and digital wallet payments, so everyone can choose the method that works best for them.
- Technology Integration: These systems use barcode scanners and advanced sensors, sometimes with computer vision or RFID, to accurately identify and process items, improving both speed and accuracy.

Consumer Electronic Equipments
Consumer electronics are the gadgets people use every day for things like entertainment, communication, and managing household tasks. These devices, such as televisions, smartphones, and digital cameras, rely on digital technology to process information and perform various functions. Over time, these gadgets have changed a lot. They started as simple analog devices but have evolved into complex digital systems that offer better performance, improved connectivity, and a much better user experience. Today, most consumer electronics, including smart devices and home appliances, use digital computing as a key part of their design.
Key Features:
- Everyday Use Devices: Consumer electronics include things like TVs, game consoles, mobile phones, and audio systems that we use regularly in our homes.
- Communications & Connectivity: Modern gadgets, like smartphones and smart TVs, are internet-connected. This lets you communicate, stream content, and use online features.
- Smart Technology Integration: Many devices now have smart features. These include things like voice control, app support, and automation, making them more convenient and versatile.
Digital Televisions
Digital TVs use digital signals to deliver clear pictures and crisp sound. Unlike old analog TVs, digital TVs process data in bits (0s and 1s) to give you better image and audio quality. This shift to digital broadcasting means stations can send multiple channels using the same frequency, making it more efficient. It also opens the door to extra features like interactive guides and richer colors.
Key Features:
- Better Picture & Sound Quality: Digital TVs offer clearer images and better sound than analog TVs.
- Efficient Signal Use: Digital signals let stations broadcast more channels on the same bandwidth.
- Extra Features: Digital TVs support features like on-screen guides, DVR, and additional content services.
Digital Pianos
Digital pianos are modern instruments that use electronic technology to replicate the sound and feel of an acoustic piano. Instead of using strings and hammers, they play high-quality recorded piano sounds through built-in speakers when you press a key. Many models offer extra features like volume control, headphone jacks, and connections for recording or learning apps, making them perfect for practice and performances at home. Digital pianos are lighter, more affordable, and easier to maintain than traditional pianos, making them a great choice for players of all skill levels.
Key Features:
- Weighted or velocity-sensitive keys: Digital pianos often have weighted keys, which make them feel more like an acoustic piano and allow for better expression and touch.
- Sound sampling & DSP: These pianos use sounds from real pianos and digital technology to create realistic tones and effects.
- Built-in functions: Many digital pianos come with volume control, headphone jacks, MIDI/USB ports, and extra instrument voices, offering more flexibility for practice, performance, and recording.
Weighing Scales
Digital weighing scales are examples of digital computers that designed to measure weight or mass. They work by converting the pressure from an object or person on the scale’s platform into a digital reading. Inside the scale, sensors called load cells detect small changes in force and send this information to a processor. The processor then turns these signals into a clear digital number, which you can easily read on the display. These modern scales are more accurate, faster, and easier to use than the old mechanical ones.
Key Features:
- High Precision Load Cells: Load cells inside the scale measure weight changes accurately and convert them into electrical signals.
- Digital Signal Processing: The sensors’ analog signals are turned into digital values by a microcontroller, allowing the scale to display weight on a screen.
- User-Friendly Display: Digital scales show weight in clear numbers, often with options to switch between units like kg or lb. Advanced models may also show additional features like BMI or even connect to your smartphone.
Conclusion
In this guide, we’ve looked at examples of digital computers impact our everyday lives, from smartphones and laptops to banking systems and weighing scales. These devices make it easier, faster, and more accurate to complete tasks. As technology keeps advancing, digital computers will continue to improve the way we work, play, and communicate.
My advice is to stay curious and learn about how these digital tools work because they’re part of almost everything we do today. The more we know, the better we can use them!Keep an eye out for more! Stay curious and keep exploring!
FAQs about Examples of digital computers
Explore the following common questions and answers about examples of digital computers:
These are 10 examples of digital computers:
- Smartphones
- Personal Computers (PCs)
- Laptops
- Tablets
- Smart TVs
- Digital Cameras
- Digital Watches
- ATMs
- Gaming Consoles
- Cars (Modern ones)
Here are 5 examples of digital devices:
- Smartphones – These are used to communicate and access different apps.
- Laptops – Portable computers for work, study, and entertainment.
- Tablets – Touchscreen devices for browsing, media, and games.
- Smartwatches – Worn on the wrist, these track fitness and display notifications.
- E-readers – Devices used for reading books or documents digitally.
A digital computer is a machine that processes information using numbers, often in the form of 0s and 1s. For example, a calculator is a digital computer that helps you with arithmetic, or a smartphone, which you can use for communication and learning.
A laptop is an example of a digital computer. It uses digital technology to perform tasks like word processing, browsing the internet, and running applications.
An example of a digital machine is a digital camera. It captures and stores images and videos in digital format, making it easier to share and edit them.
At home, digital computers include smart TVs, digital clocks, tablets, and home appliances with digital controls. These devices process digital signals to show images, keep time, or run programs. They make daily life more convenient and connected.
In business, common examples of digital computers include servers, office desktops, and banking systems that store and manage large amounts of information. These computers help with accounting, customer data, online transactions, and data analysis. They make work faster and more organized.
In schools, students and teachers use personal computers and laptops to write documents, watch lessons, and research topics online. Digital tablets and classroom computers help with interactive learning and assignments. All of these rely on digital computing to support education.

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks