Why Embedded Computers are Important in Modern Technology
Published: 17 Dec 2025
Embedded computers are everywhere, from the smartphones in our pockets to the cars we drive. They play a useful role in making everyday devices smarter and more efficient.In this guide, we’ll take a closer look at how embedded computers work, the different types and the industries that rely on them.By the end, you’ll have a solid understanding of how these systems power much of the technology around you.Let’s get started!
What is an Embedded Computer?
An embedded computer is a specialized computer designed to work a specific task within a larger system.Unlike regular computers that can run multiple applications, an embedded computer is focused on one job and works within the device it is part of.These systems are often built into everyday objects like washing machines, cars and medical equipment.They are small, efficient, and designed to run continuously with minimal user interaction. Actually, embedded computers help make devices smarter by controlling functions and processing data.

Importance of Embedded Computers
Embedded computers are important in modern technology, playing a basic role in making devices smarter and more efficient.They allow for automation, control, and real-time processing in countless applications.Here’s why they are so important:
- They enable devices to perform specific tasks with high efficiency.
- They are energy-efficient, using less power than general-purpose computers.
- They are dependable and can operate 24/7 without much maintenance.
- They make everyday devices, like smartphones and home appliances, smarter.
- They allow for real-time data processing, which is critical in fields like healthcare and automotive.
How Embedded Computers Work
An embedded computer works by controlling specific functions within a device, using both hardware and software to perform its tasks. It operates behind the scenes, often without the user even knowing it’s there. Here’s how it works:
- The embedded computer receives input data from sensors or devices (e.g., temperature sensors, buttons).
- It processes the input data using its central processing unit (CPU).
- The computer then makes decisions based on pre-programmed instructions or algorithms.
- After processing, it sends output commands to control the device’s functions (e.g., turning on a motor or displaying data on a screen).
- It works continuously, running the same task over and over with little to no interruption.
- The system is often designed to be efficient, using minimal power while running reliably for long periods.

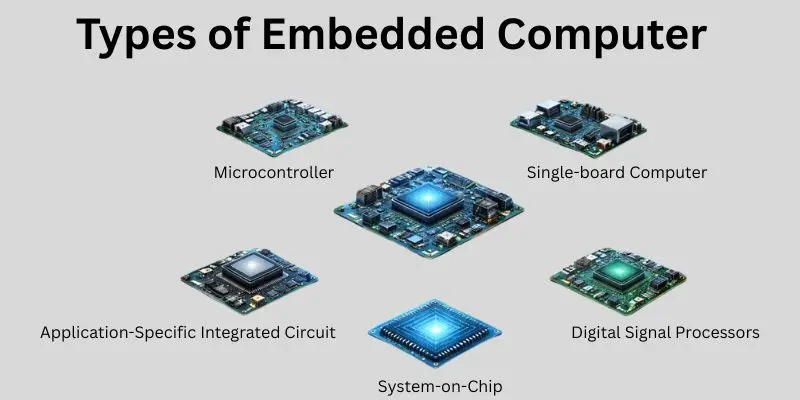
Types of Embedded Computers
There are different types of embedded computers, each designed for specific purposes. These systems vary in size, performance and complexity depending on the tasks they need to perform.Here are the main types:
- Microcontroller-based Embedded Computers: Small and low-power systems used for simple tasks like controlling devices or reading sensors.
- Single-board Computers (SBCs): Compact computers on a single board, often used in robotics, automation and educational projects.
- System-on-Chip (SoC): A single chip that integrates the CPU, memory and other essential components, commonly found in smartphones and smart devices.
- Application-Specific Integrated Circuits (ASICs): Custom chips designed for specific tasks, offering high performance for applications like video or data processing.
- Digital Signal Processors (DSPs): Specialized embedded computers that handle real-time data processing, often used in audio, video or communication systems.
Core Parts of an Embedded Computer
Embedded computers consist of many important parts that work together to complete particular tasks.These parts ensure the system is efficient, reliable and able to carry out its functions.Here are the core parts of an embedded computer:
- Microcontroller or Processor: The brain of the system, responsible for processing data and executing instructions.
- Memory: Stores data and program instructions.This includes RAM (temporary storage) and ROM/Flash (permanent storage).
- Input/Output Interfaces:These allow the embedded computer to communicate with external devices, like sensors, buttons or displays.
- Power Supply: Provides the necessary energy for the system to function, often designed to be low-power for efficiency.
- Sensors and Actuators: Sensors get data from the environment, while actuators carry out actions based on the processed data, like turning on a motor or adjusting a valve.
- Communication Modules: Allow the system to connect with other devices or networks, using protocols like Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, or Ethernet.
Key Features & Characteristics
Embedded computers are designed for specific tasks and are optimized for efficiency and reliability.Here are some of their key features and characteristics:
- Dedicated Functionality: Embedded computers are built to perform a specific function or set of tasks within a larger system.
- Compact Size: They are small and often integrated into other devices, making them ideal for space-constrained environments.
- Low Power Consumption: These technologies were created to consume minimum power, which is useful for battery-powered devices.
- Real-time Processing: Many embedded computers operate in real-time, meaning they process data and make decisions instantly to control devices like safety systems or robotics.
- Reliability: They are built to run continuously with minimal maintenance, making them highly reliable for long-term use.
- Cost-effective: Because they are designed for a single purpose, embedded systems are often cheaper to produce than general-purpose computers.
- Limited User Interaction:Unlike regular computers, embedded systems typically do not require user input once set up, running automatically in the background.
Uses of Embedded Computers
Embedded computers are used in a large range of industries and devices, making everyday technology smarter and more efficient.They play a helpful role in automating processes, improving performance and enabling advanced features.Here are some common applications:
- Consumer Electronics: Found in devices like smartphones, smart TVs, and wearable gadgets to handle specific functions like processing signals or controlling user interfaces.
- Automotive Industry: Used in car systems for tasks such as controlling engine functions, managing safety features, and operating navigation systems.
- Healthcare Devices: Embedded computers are used in medical equipment like pacemakers, diagnostic machines and monitoring systems to make sure accurate readings and reliable performance.
- Industrial Automation: These systems control machinery, robots and other automated equipment in factories, ensuring efficient production and safety.
- Smart Home Devices: Embedded computers power devices such as thermostats, smart locks, and home security systems, allowing for automation and remote control.
- Aerospace and Defense: Used in navigation systems, radar and communication systems to support mission-critical operations.
- IoT Devices: Embedded computers are the foundation of Internet of Things (IoT) devices, enabling smart cities, connected home devices and environmental monitoring.
- Networking Equipment: Found in routers, switches, and firewalls, where they help manage data traffic and ensure secure communication.
- Entertainment Systems: Used in gaming consoles, audio systems, and streaming devices to process data and manage system functions.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Embedded Computers
In this section, we will look at the pros and cons of embedded computers to understand their strengths and limitations.
| Advantages of Embedded Computers |
|---|
|
| Disadvantages of Embedded Computers |
|---|
|
Key Considerations When Choosing an Embedded Computer
Choosing the right embedded computer depends on the specific requirements of your project or application.It’s important to consider various factors to ensure the system meets both performance and efficiency needs.Here are some key considerations to keep in mind:
- Performance Requirements: Determine the computing power needed for the tasks the embedded computer will handle.
- Size and Form Factor:Choose a system that fits the available space in the device or machine.
- Power Consumption:Consider how much power the system will use, especially for battery-operated devices.
- Cost: Balance the budget with the performance and features needed for the application.
- Reliability: Make sure the embedded system is robust enough to operate continuously without failure.
- I/O Interfaces: Check if the system has the necessary input and output ports for sensors, actuators and communication.
- Customization and Scalability: Decide if the system needs to be customizable or scalable for future upgrades.
- Real-Time Processing: Ensure that the embedded computer can process data in real-time if your application demands it.
- Operating Environment: Consider whether the system needs to operate in extreme conditions, like high temperatures or humidity.
The Future of Embedded Computing
The future of embedded computing is filled with amazing advancements that will continue to change the technology we use every day. As industries demand smarter, faster and more efficient systems, embedded computers will play an even bigger role in driving innovation.Here’s a look at what the future holds for embedded computing:
- Integration with IoT: when the Internet of Things (IoT) expands, embedded computers will become the backbone of smart homes, cities and industries, enabling seamless device communication and data exchange.
- Edge Computing: Embedded systems will increasingly support edge computing, where data is processed locally instead of relying on cloud servers, leading to faster and more efficient operations.
- AI and Machine Learning: Embedded systems will incorporate AI to enable smarter decision-making and autonomous operations, especially in fields like healthcare, automotive and robotics.
- Increased Power Efficiency: With a focus on sustainability, embedded computers will become even more energy-efficient, extending battery life for portable and remote devices.
- Miniaturization: As technology advances, embedded computers will continue to shrink in size, making them even more versatile and capable of fitting into a wider range of devices.
- 5G Connectivity: The rollout of 5G will improve the capabilities of embedded systems, allowing them to handle faster data transfer and support more connected devices in real-time.
- Security Improvements: With the rise in connected devices, embedded systems will feature enhanced security measures to protect sensitive data and prevent cyber threats.
Conclusion
In this guide, we’ve explored the world of embedded computers, from understanding their core components to discovering the many applications they power. We’ve also looked at the key factors to consider when choosing an embedded system and the exciting future developments ahead.
If you’re diving into embedded computing, it’s important to keep in mind how these systems impact everyday technology and industries.Whether you’re building a simple project or working on advanced tech, knowing about embedded computers will help you make better decisions and stay ahead.So, folks, keep learning and exploring all the amazing things embedded computers can do! Stay curious!
FAQs
An embedded computer is used to perform specific tasks within a larger device or system. For example, it might control a washing machine’s settings or manage a car’s safety features. It’s designed to do one job very efficiently and reliably.
A microcontroller is a small chip with a CPU, memory and input/output interfaces, typically used in embedded systems. An embedded computer is a complete system, often more complex, that includes a microcontroller or processor to run specific tasks.
Yes, you can build your own embedded computer, especially with platforms like Raspberry Pi or Arduino.These tools offer easy-to-use hardware and software for beginners and hobbyists to create their own embedded systems.
Platforms like BeagleBone, Raspberry Pi and Arduino are great for beginners.They offer simple tools and large communities to help you get started with embedded systems projects.
Embedded computing is crucial in industries like automotive, healthcare, consumer electronics and industrial automation.It’s used in devices like cars, medical equipment, smartphones and robots.
Embedded systems are created for particular purposes within a larger system, while regular computers can handle a wide range of applications.Embedded systems are smaller, more efficient and optimized for a particular job.
Smartphones are not entirely embedded computers, but they do contain embedded systems. For example, the chip controlling the camera or battery management is an embedded computer designed for specific functions within the phone.
Common programming languages for embedded development include C, C++, and Python. These languages are used to write software that interacts directly with the hardware to control devices.

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks