What Is Line Printer? Everything You Need To Know
Published: 17 Oct 2025
Ever wondered how offices are used to print hundreds of pages in just a few minutes? It sounds impossible without modern printers, right? Don’t worry, there’s a office use printer powering that speed. In this article, we’ll look at the line printer, how it works, its main parts, and where it’s still useful today. By the end of this article you’ll realize why this famous printer changed businesses and data centers.
What is a Line Printer?
A line printer is a high-speed impact printer that creates one full line of text at a time. It was mostly used in large offices, banks, and data centers to handle massive print jobs. Instead of printing each character separately it produces the full line at once, which is much faster than classic printers. It uses a drum or chain device to strike inked ribbons against paper. Line printers are known for their speed, durability, and stability for printing huge reports or bills. They are less common today, but remain valuable in businesses that need fast and continuous printing.
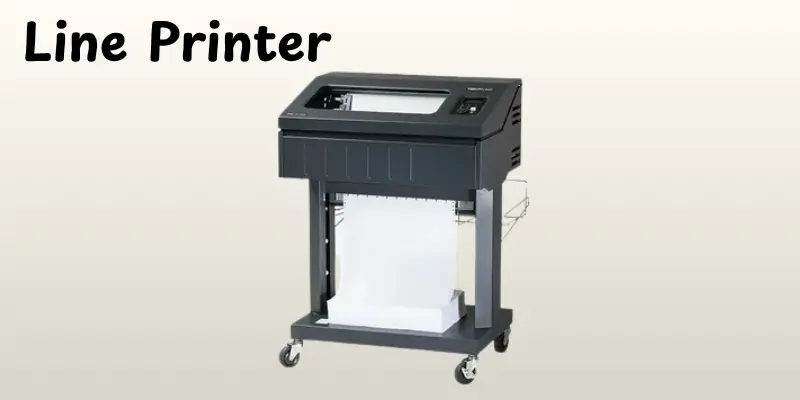

Short History of Line Printers
The line printer was invented in the 1950s, during the early days of computers, when huge data processing systems required fast printing. It was created to handle large print work, particularly for business reporting and billing. The first popular versions used drum and chain machines to print full lines at once. In the 1960s and 1970s, businesses like IBM modified the design to make it quicker and more reliable. While modern laser and inkjet printers have replaced them in most offices, line printers continue to be used in businesses that require high-speed, continuous printing.
How Does a Line Printer Work?

A line printer prints the complete line of text at once instead of printing every character separately. It’s designed for speed and is often used in situations where big amounts of data must be produced fast. Let’s have a look at how it works in simple steps.
- The printer receives data from the computer in the form of text lines.
- It stores the data in its memory buffer before printing.
- A print drum, chain, or band moves continuously inside the printer.
- As the paper moves forward, the correct characters on the drum or chain align with the ink ribbon.
- Small hammers behind the paper strike the ribbon to print the characters onto the page.
- The process repeats for each line until the entire document is printed.
- The printer then automatically feeds the paper for the next set of lines.
Key Components of a Line Printer
A line printer is made of many important parts that work together to print a whole line at once. Each component plays a key role in producing clear, fast, and continuous prints. Here are the main parts explained simply:
- Print Drum or Chain: Holds all the characters used for printing and rotates to align the correct one for each position on the paper.
- Hammers and Magnets: Small hammers strike the ribbon through the paper to print characters, controlled by magnets.
- Ink Ribbon: A long strip of inked fabric that transfers ink onto the paper during printing.
- Paper Feed Mechanism: Moves the paper forward after each line is printed to prepare for the next one.
- Control Unit: Manages the timing and movement of all parts, ensuring accurate and smooth printing operations.
Types of Line Printers
Line printers may be classified into different types based on how they print characters on paper. Each type uses a slightly different strategy but shows the same goal: print one whole line at a time, fast and clearly. Here are the most common types, explained simply:
- Drum Printer: Uses a rotating drum with characters engraved on it; prints when the right character aligns with the hammer.
- Chain Printer: Has a moving chain of characters that passes in front of the paper and ribbon, printing when the hammer strikes.
- Band Printer: Uses a flexible metal band with characters on it, printing as the band moves rapidly across the line.
- Bar Printer: Prints by striking a full row of pins or bars against the ribbon to form a line of text.
- Wheel Printer: Uses a circular wheel with characters on its outer edge; prints one character at a time as the wheel rotates and a hammer strikes it.
Uses of Line Printers
Line printers are mostly used in situations that need high-speed printing and large amounts of output. They are designed for tasks where speed is more important than physical design.Here are some common applications of line printer:
- Banking Systems: Used to print transaction logs, statements, and reports.
- Billing Departments: Helps in generating large numbers of bills and invoices quickly.
- Industrial Reports: Ideal for printing daily production or machine data reports.
- Airline and Railway Offices: Prints passenger lists, tickets, and schedules efficiently.
- Government Offices: Used for preparing forms, records, and data summaries.
- Data Centers: Handles large-scale printing of computer-generated reports.
- Warehouses: Prints stock lists, packing slips, and shipment records fast.
Advantages and Disadvantages
In this section, we will look at the pros and cons of a line printer. These points will help you understand where this printer performs well and where it falls short.
| Advantages of Line Printer |
|---|
|
| Disadvantages of Line Printer |
|---|
|
Tips for buying a Line Printer
If you want to buy a line printer, you need to know what features to look for before you spend any money. Here are some basic tips to help you select the best one for your requirements.
- Printing Speed: Check how many lines per minute (lpm) the printer can handle. Faster models save time for bulk printing.
- Print Quality: Choose a printer that offers clear and readable text, especially if reports need to be professional.
- Noise Level: Some line printers are loud; look for quieter models if you work in an office setting.
- Durability: Go for a strong and long-lasting printer if you’ll use it daily in a high-volume environment.
- Paper Handling: Make sure it supports the type and size of paper you use regularly.
- Maintenance and Parts: Pick a printer with easy-to-find ribbons, hammers, and other spare parts.
- Connectivity: Ensure it can connect to your computer system using modern ports or network options.
- Cost and Warranty: Compare prices and choose one that fits your budget but still offers a good warranty.
Conclusion
So, in this essay, we’ve looked over the line printer completely. We explored its definition, main elements, types, functions, benefits, limitations, and applications. My suggestion: If you need a fast, durable printer for high-volume uses, a line printer is an excellent choice; it saves time and handles huge workloads easily. Try it in the office or business setting and see the difference for yourself. Keep learning, close friends, and stay up to speed with useful tech tips!
FAQs
Line printers print quickly and effectively, even with high volumes. They are powerful and reliable for continuous use. They also maintain low operating expenses as compared to other printers.
Line printers were often used in banks, offices, and data centers. They produced reports, invoices, and huge documents quickly. They were used in any location that required high-volume printing.
A line printer produces one complete line of text at a time. It prints with hammers, ribbons, and paper. The printer presses the ribbon on the paper to produce letters.
The five basic types of printers are drum, chain, band, bar, and wheel. Every type has a unique technology to produce lines fast. They are all focused on speed and efficiency.
Line printers can produce hundreds or thousands of lines per minute. The actual speed of the printer is determined on its model and type. They work more quickly than dot matrix and daisy wheel printers.
Yes, multiple industries continue to use line printers for high-volume printing. They are most commonly found in banks, government offices, and big companies. Laser and inkjet replacements have reduced their use in modern businesses.

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks