What is Optical Mark Recognition (OMR)? Key Benefits and Uses
Published: 3 Feb 2026
Optical Mark Recognition (OMR) is a technology that allows for the automated reading of marks made on paper forms. By detecting marks such as checkboxes, bubbles, and filled-in circles, OMR systems convert physical data into digital form for easier analysis. This technology is commonly used in areas like education, surveys, and elections, where large volumes of data need to be processed quickly and accurately.
The main advantage of using OMR technology is its efficiency. Instead of relying on time-consuming and error-prone manual data entry, OMR scanners can process hundreds or thousands of forms in a short amount of time. This makes it a valuable tool for businesses and organizations looking to streamline their data collection and processing.
As OMR technology continues to evolve, modern solutions now include cloud-based OMR platforms and mobile OMR applications. These advancements have made OMR systems more accessible and flexible, allowing users to capture data from anywhere and at any time.
What is Optical Mark Recognition (OMR)?
Optical Mark Recognition (OMR) refers to the process of scanning and interpreting marks, such as checkboxes, bubbles, or filled circles, on paper forms. These marks are then translated into digital data for easy analysis. OMR technology is designed to detect marks in predefined areas on forms, making it an excellent tool for large-scale data collection without human input.
OMR is used across many fields. In education, it helps grade multiple-choice exams quickly. In surveys, it collects responses efficiently. By automating data entry, OMR saves time and reduces human errors that are common in manual data entry.

Understanding Optical Mark Recognition Technology
OMR technology works by using light reflection to detect marks on paper. When light is projected onto a document, areas that are marked reflect less light than blank spaces. OMR software analyzes these light patterns to identify the marks. This simple yet effective system allows for fast data extraction from documents.
The technology relies on specialized OMR scanners that read these light variations. These scanners capture the marks on the form, and OMR processing software converts them into digital data, making it easy to store and analyze the information.
How OMR Works
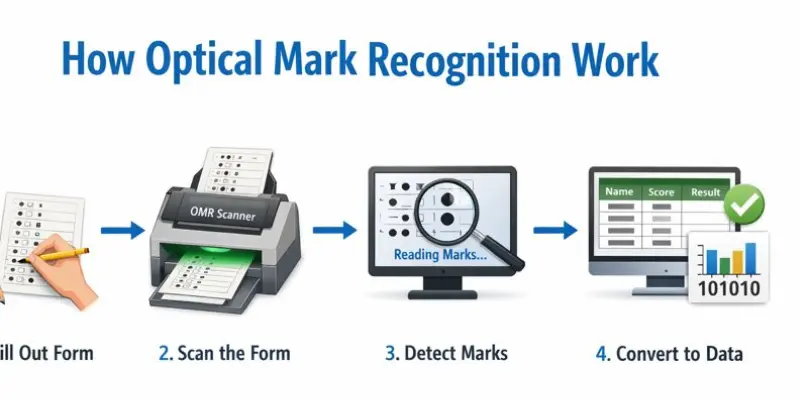
The process of how OMR technology works is straightforward. First, a specially designed form is created with specific areas marked for responses. The user fills out the form, making sure to mark the correct answers or selections. Afterward, the form is scanned by an OMR scanner, which detects the marks.
The scanned data is then processed by OMR software. The software converts the marks into digital data, which can be used for analysis, grading, or reporting. This entire process is much faster than manual entry and reduces the chances of errors.
Key Components of OMR
To understand OMR technology, it’s essential to know the key components involved. The three primary elements of an OMR system are the OMR sheet, the scanner hardware, and the processing software.
The OMR sheet is a specially designed form with pre-defined areas for responses. The scanner hardware reads the marks on the sheet, and the OMR processing software interprets the data. Together, these components work seamlessly to convert physical marks into usable digital data.
Mark Detection Techniques
Mark detection is the process by which OMR systems identify and classify marks on forms. There are several techniques used in OMR technology to ensure accuracy. The most common are pixel counting, adaptive thresholding, and pattern recognition.
Pixel counting measures the darkened areas within a predefined space. Adaptive thresholding adjusts for variations in the mark’s intensity, ensuring consistent recognition. Pattern recognition goes a step further by analyzing the shape and position of marks, which helps improve accuracy, even with imperfect markings.
Difference Between OCR and OMR
While both OCR (Optical Character Recognition) and OMR involve reading data from paper, they serve different purposes. OCR is used to recognize characters and text, while OMR focuses on detecting marks made in predefined areas.
OMR technology is much simpler and faster than OCR, as it only detects whether a mark is present, rather than interpreting text. This makes OMR ideal for forms with structured responses like multiple-choice questions or survey answers.
Most Common Applications of OMR Technology
OMR technology is widely used across several industries. One of its main applications is in educational assessments, where it is used to grade tests and exams efficiently. Another common use is in survey data collection, where it helps process large volumes of survey forms quickly.
Other industries that benefit from OMR technology include elections, where it’s used for ballot counting, and healthcare, where OMR systems are used to process medical forms and patient data efficiently.
Educational Assessments and Exams
In education, OMR technology is used extensively to grade multiple-choice tests and standardized exams. It eliminates the need for manual grading, which can be time-consuming and prone to error. OMR processing software allows institutions to handle large numbers of tests in a short amount of time, increasing efficiency.
OMR systems also help educational institutions track student performance over time by grading quizzes and assignments quickly. This allows for more frequent assessments, providing timely feedback to students.
Survey Data Collection
In the world of survey data collection, OMR technology plays a vital role. Whether it’s for market research, public opinion polls, or customer feedback, OMR systems provide a fast and reliable way to capture data from paper forms. By scanning completed forms, OMR scanners can process hundreds or thousands of responses in hours, enabling researchers to analyze data quickly and make informed decisions.
With OMR technology, organizations can gather large amounts of data without relying on manual entry, which is prone to human error. This improves the overall accuracy and efficiency of the data collection process.
Election Ballot Counting
OMR technology is widely used for election ballot counting, where its speed and accuracy are crucial. OMR scanners are used to process and count ballots quickly, ensuring that results are available much faster than traditional counting methods. The technology can handle large volumes of ballots, providing accurate and verifiable results.
In addition to its speed, OMR technology helps reduce human error in counting, ensuring that the election process is fair and transparent. This makes OMR a trusted tool in modern elections.
Modern Optical Mark Reader Software
OMR software has evolved significantly in recent years. Modern OMR software offers a wide range of features, including enhanced mark detection, improved error correction, and real-time data processing. These advancements make OMR systems more efficient and versatile than ever before.
Many OMR software solutions also come with cloud-based capabilities, allowing for easy integration with other systems and enabling users to process forms remotely. This shift to cloud-based OMR platforms has revolutionized data collection, making it more accessible and scalable.
Cloud-based OMR Platforms
Cloud-based OMR platforms have made OMR technology more accessible and cost-effective. These platforms allow organizations to scan and process OMR forms without needing expensive hardware. With cloud integration, users can access their data from anywhere and ensure real-time processing of forms.
Cloud-based solutions also enable easier sharing of data and collaboration, as the processed data can be accessed remotely by different teams. This flexibility makes OMR technology even more valuable for businesses and organizations.
Mobile OMR Applications
Mobile OMR applications have brought greater flexibility to OMR technology. With mobile devices like smartphones and tablets, users can now scan and process OMR forms on the go. This is especially useful for field data collection, such as in surveys or exams conducted in remote locations.
Mobile OMR apps offer real-time data processing and automatic correction of scanned forms. This improves the accuracy of data capture and ensures timely results, whether for education, healthcare, or market research.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Optical Mark Recognition
In this section, we will look at the pros and cons of Optical Mark Recognition (OMR) to help you understand its strengths and weaknesses.
| Advantages of Optical Mark Recognition |
|---|
|
| Disadvantages of Optical Mark Recognition |
|---|
|
What You Need to Know Before Implementing OMR Technology
Before implementing OMR technology, there are several factors to consider. One of the most important is the form design requirements, as poorly designed forms can lead to inaccurate data collection. Ensuring that forms are properly aligned and the marks are clear is crucial for accurate results.
You also need to choose the right OMR scanners and software. The scanner specifications should match the resolution and quality required for your forms. Finally, you must establish a data processing workflow to ensure smooth and efficient handling of the collected data.
Form Design Requirements
Proper form design is key to ensuring the accuracy of OMR technology. The form must be designed with the right spacing, bubble size, and alignment to ensure that the OMR scanner can easily detect the marks. Using standardized templates can help achieve consistent results across different forms.
Considerations like bubble placement, font size, and the inclusion of instructions are critical. These factors contribute to the OMR accuracy rate, ensuring that forms are processed smoothly.
Scanner Specifications
Choosing the right OMR scanner is essential for ensuring accurate data capture. The scanner should have the right resolution (typically 300 DPI) to capture the fine details of the marks. High-quality scanners help reduce errors and improve the overall speed of the data processing workflow.
OMR scanners also need to be compatible with OMR processing software to ensure seamless integration. This allows for efficient data collection and faster results.
Data Processing Workflow
The data processing workflow in OMR systems includes several key steps, from scanning the forms to analyzing the data. After the forms are scanned, the OMR software interprets the marks, cleans up any errors, and generates reports. This workflow ensures that data is captured accurately and quickly, without the need for manual intervention.
Automation of the data processing workflow reduces human errors and significantly speeds up the entire process. It’s especially useful in environments like education and survey data collection, where large volumes of forms need to be processed.
Quality Control Measures
Maintaining OMR accuracy requires robust quality control measures. This includes scanning forms at the appropriate resolution, using consistent templates, and verifying that forms are aligned correctly. Regular calibration of OMR scanners is also essential to ensure consistent performance.
Error-checking mechanisms in OMR software can also identify potential issues, such as unfilled bubbles or misaligned marks. By implementing these quality control measures, organizations can maintain a high level of accuracy throughout the data collection process.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Optical Mark Recognition (OMR) is an invaluable tool for organizations that need to handle large volumes of structured data quickly and accurately. Whether in education, surveys, elections, or medical forms, OMR technology offers unmatched speed, accuracy, and efficiency. By implementing OMR software, businesses can streamline their data collection processes and focus on higher-value tasks that contribute to their success.
FAQs
Optical Mark Recognition (OMR) is a technology used to automatically detect marks made on paper forms. It is commonly used to read checkboxes, bubbles, and ticks. OMR converts these marks into digital data, making it easier to analyze large amounts of information quickly and accurately.
OMR works by shining light onto a document and detecting the light reflected by the marks. Darkened areas, such as filled checkboxes, reflect less light than unmarked areas. This difference in light reflection is processed by OMR scanners and converted into digital data for analysis.
OMR is widely used in educational assessments, like standardized tests, to quickly grade exams. It is also used for surveys, election ballot counting, and medical form processing. The technology is particularly helpful for collecting and analyzing large volumes of data with high accuracy.
OMR detects marks in predefined areas on a form, such as checkboxes or bubbles, while OCR (Optical Character Recognition) reads and interprets printed text. OMR is simpler and faster, making it ideal for forms with structured responses like multiple-choice questions, while OCR works with text-based documents.
Cloud-based OMR platforms allow users to process forms without needing dedicated hardware. They offer flexibility, allowing for easy access and real-time data processing from any device with internet access. These platforms are also cost-effective, as they eliminate the need for expensive physical scanners.
Yes, OMR can be used on mobile devices through specialized apps. These apps use the camera on smartphones or tablets to scan and process OMR forms. Mobile OMR applications make it convenient for users to capture and analyze data on the go, making it ideal for field surveys or education.
OMR detects marks made on paper, like checkboxes or filled circles, whereas OCR reads printed text. OMR is great for structured forms like surveys and exams, while OCR is used to convert printed or handwritten text into editable digital data. Both are used for data extraction but for different purposes.
OCR, or Optical Character Recognition, is a technology that converts printed or handwritten text into machine-readable data. It scans documents and recognizes characters to create editable text. OCR is commonly used for digitizing books, invoices, and forms to automate data processing.

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks